Farsightedness (Hyperopia)
What is Farsightedness (Hyperopia)?
The farsightedness is a common eye condition, in which the distant objects are seen clearly, but at close distance the image may be blurry and unclear. Usually the farsightedness appears during childhood and lasts for the whole life.
Farsightedness
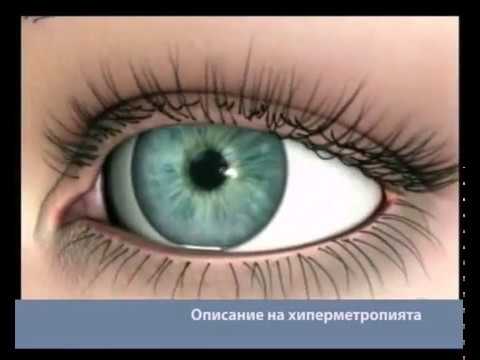
Farsightedness
Normal eye

Normal eye
The degree of farsightedness affects the ability to focus. People with high degree of farsightedness can see clearly only objects at far distance, while patients with lower degree may be able to see clearly objects at closer distance.
The farsightedness is often present from birth and is passed from parent to child. The condition may be easily corrected with glasses or contact lenses. Another successful method is laser correction of farsightedness.
Vision in Farsightedness (Hyperopia)
People with farsightedness have problems with seeing at close distance, including when reading and working with computer. The hyperopia is a condition of the eye in which light is focused behind, instead of on the retina and as a result the close objects may be seen unclear. The reasons for the appearance of farsightedness may be different: axial shortening of the eyeball, flat lens or reduced curvature of the cornea, age changes.
The patients with farsightedness may compensate the need of glasses by straining the eyes, which often results in headache, especially in case of continuous work at close distance. Depending on the degree of the condition and the age of the patient, the far vision may also be blurred.
Symptoms of Farsightedness (Hyperopia)
If you have farsightedness, you may experience the following symptoms:
- The close objects may be blurry
- Crossing the eyes n order to see clearly
- Tiredness, redness and pain in the eyes or around them
- General eye discomfort or headache following continuous straining at close distance, such as reading, writing, work with computer or drawing
The farsightedness is often diagnosed during childhood or between the early school years to the teenage years. The children with farsightedness prefer outdoor games, instead of playing inside with smaller toys. A child with farsightedness may have the following symptoms:
- Frequent blinking
- Frequent appearance of eye styes
- Fast eye fatigue, headache and blurred vision
- Increased eye watering without reason
Types of Farsightedness (Hyperopia)
The degree of farsightedness is determined by the optical power of the eye measured in diopters – the higher the diopter, the further behind the retina is focused the image. Depending on the method of measurement of the optical power of the eye, there are several types of farsightedness. The correlation between them shows what part of the patient’s dioptric power needs correction for better vision (especially at close distance), and what part is still undetermined (often causing headache).
- Low farsightedness: up to +2.0 D
- Moderate farsightedness: from +2.0 D to 5.0 D
- High degree of farsightedness: more than 5.0 D
- Manifest hyperopia: measured with dilated pupils
- Total hyperopia: measured with constricted pupils
- Latent hyperopia: determined by extracting the manifested hyperopia from the total hyperopia
Treatment of Farsightedness (Hyperopia)
For patients at age 18 – 40 years the preferred treatment is laser correction of farsightedness (hyperopia). This method is completely safe, bloodless and sutureless. You can find more information at Laser correction of Farsightedness (Hyperopia).
In patients above 40 years of age there is another method for correction of farsightedness (hyperopia). The implantation of soft multifocal lenses offers excellent vision and prevention of eye diseases, which may appear with the age.
Laser correction of Farsightedness (Hyperopia)
Eye Clinic Luxor has many years of experience in treatment of farsightedness with laser correction of the vision, or with implantation of multifocal lenses. More than 30 000 patients trust our professionalism each year, as more than 2000 patients are operated in the hospital. Depending on your age, vision and specific needs, we can offer you the best option for your excellent vision.
Other refractive errors
In addition to farsightedness (hyperopia), other refractive errors are: